Choosing the best cloud model for your business
Simply put, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. You typically pay only for cloud services you use, helping lower your operating costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently, and scale as your business needs change. 1
A Tech Pro Research survey revealed that 38% of companies are already using industry cloud services, and 19% plan to do so within the next 12 months, making a solid majority of 57% either using or planning to use industry cloud services. Another 23% of respondents said they are considering it, but they haven’t set a timeline for adoption. This means that only 20% have completely ruled out industry cloud services.2
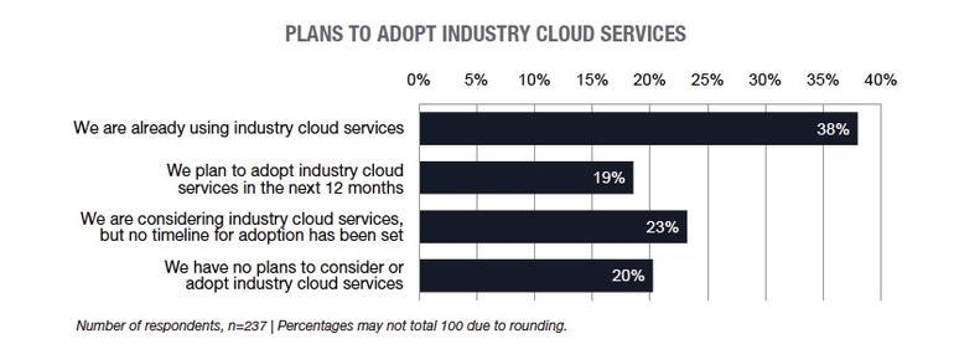
Image: Tech Pro Research
However, not all clouds are the same and not one type of cloud computing is right for everyone. Several different models, types, and services have evolved to help offer the right solution for your needs. First, you need to determine the type of cloud deployment, or cloud computing architecture, that your cloud services will be implemented on. 1
Cloud computing spans a range of classifications, types and architecture models. The transformative networked computing model can be categorized into four major types: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud and Multi Cloud. 3
1. Public Cloud and Private Cloud
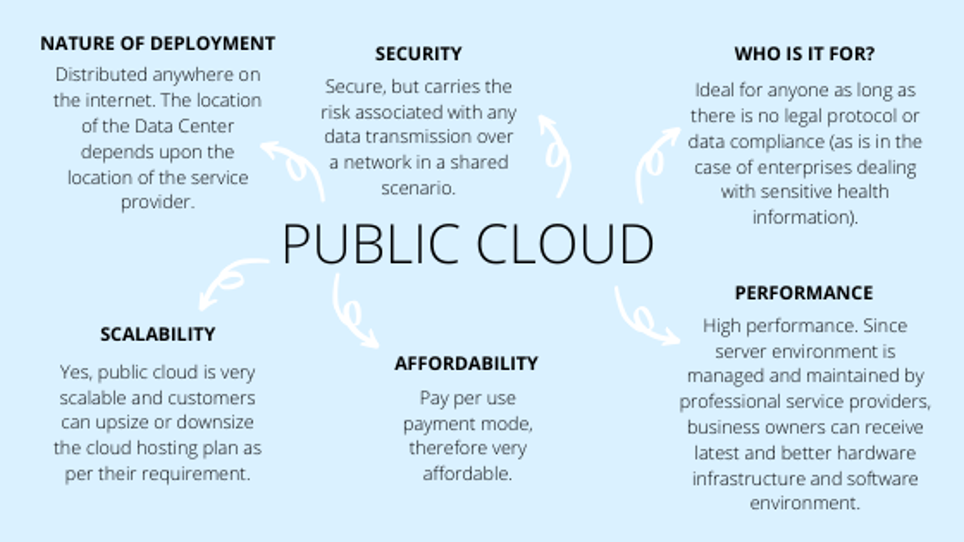
The Public Cloud, a pay per use model, is a cloud infrastructure with all the services available through the web, so the computing infrastructure can be shared among multiple organisations. This model is owned and operated by service providers.
On the other hand, the Private Cloud is a business-specific infrastructure exclusively designed for individual companies. It provides options for hosting the data either on-site or at the service provider’s data centre.
Advantages for businesses 4 :
|
Public Cloud |
Private Cloud |
|
Scalability – Virtual machines within the system can be created, scaled and shut-down in an instant. |
Enhanced security and privacy – Can be isolated from all but the company who owns it. |
|
Cost – Service can be implemented at a fraction of the cost it would take to implement a Private Cloud alternative. |
Total control – You are free to build and configure your Private Cloud in any way you like. |
|
Management – You will be free from the responsibility of maintaining and managing the infrastructure. |
Increased performance – The resources within your private cloud infrastructure are at the disposal of your company and your company alone. |
|
|
Improved reliability – Private Cloud offers a greater degree of reliability thanks to a fault resilient and redundant architecture that isn’t shared in any way. |
|
|
Increased flexibility – Virtual machine can be scaled up and down seamlessly. |
Disadvantages for businesses [5][6] :
|
Public Cloud |
Private Cloud |
|
Security – You can only customise security factors at the operating system level – security at the physical level is under the purview of your supplier and they are also by default, visible internet-wide leading to the increased levels of remote scanning for vulnerabilities. |
Cost – With exclusivity comes increased cost. |
|
Inflexibility – Although virtual machines are very flexible in terms of scale and power, some choices may be made for you by the hosting provider. |
Under-utilisation – With a private cloud, the cost of capacity under-utilisation is a cost to you, not to your provider. Therefore managing and maximising utilisation becomes your concern. |
|
Compliance – Have to consider the legal requirements around data management. |
Platform scaling – Large upward changes in your requirements are likely to require scaling of the physical infrastructure. |
What kind of organisation will benefit from the Public Cloud model?
The Public Cloud model is ideal for anyone as long as there is no legal protocol or data compliance (enterprises dealing with sensitive health information). Highly suited for organisations that aren’t infrastructure-, security-specific. Also companies that would like to store non-sensitive data can utilize this model to its fullest for their operations.
What kind of organisation will benefit from the Private Cloud model?
The Private Cloud model is recommended for government agencies, hospitals or businesses handling classified data, exclusively for organisations planning to store sensitive or private data. Though expensive, this model is highly efficient, secure, and safe. 4
2. Hybrid Cloud and Multi Cloud
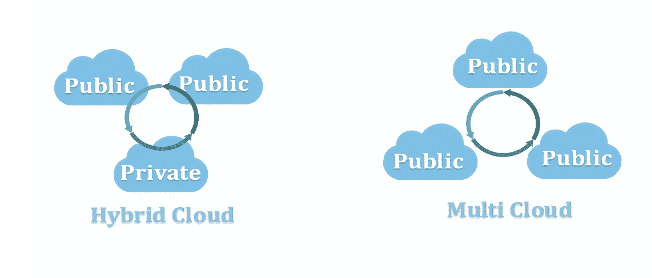
The Hybrid Cloud model is a combination of Public and Private systems. Small and medium businesses that want to leverage both cost-effectiveness and robust data security, control and privacy will invest in this type of model. 4
“Multi-cloud” describes a strategy on the other hand, while “hybrid cloud” is a new type of infrastructure.
The confusion between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud is compounded by the fact that they’re often used interchangeably. While the two terms are related, they describe two distinct (but both important) concepts. Understanding the difference can help ensure the success of your overall cloud strategy. 8
Differences between Hybrid Cloud and Multi Cloud:
|
Hybrid Cloud |
Multi Cloud |
|
The pairing of a private cloud with public cloud |
The pairing of multiple public clouds but can also incorporate physical and virtual infrastructure (including private clouds) |
|
Hybrid Cloud cannot have the multi-cloud approach |
Multi cloud may include hybrid cloud |
|
Relies on a private data centre |
Organisations may choose one service provider for IaaS and another for SaaS |
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud and Multi Cloud for businesses: 4
|
Hybrid Cloud |
Multi Cloud |
|
Security – Including private cloud in the mix gives reassurance when it comes to security of your most sensitive operations. |
Lower risk of DDoS attacks – Makes your company’s services resilient against these types attack because even if one cloud goes down, others remain available to take the load until your service recovers.
|
|
Cost efficiency – Hybrid cloud adopters can balance their need to be cost efficient with the security of keeping their most sensitive and critical workloads on private cloud. |
Power of Choice – Able to play the field and explore different providers to find the best match for each part of your business to line up its functionality for a perfect fit. |
|
Scalability – Critical data, assets, and operations can continue to reside in the private cloud, but organizations can now leverage the expansive power of cloud computing to quickly and efficiently increase their operational capacity. |
Reliability – Using multiple clouds to host your various components is the ultimate form of redundancy, making for fewer SPOFs.
|
|
Flexibility – The “pick and mix” style of hybrid cloud gives organisations the chance to explore a variety of operational directions and find the optimum cloud solution for them. |
Flexibility – By employing more than one cloud-hosting company, particularly a mix of private and public ones, you can match your needs to the solutions that fit the best, and alter them as the need fits. |
|
Preservation of investments – Enables you to continue using existing IT investments, whether on premises or co-located. |
Avoiding vendor lock-in – Avoid putting yourself in the position of having to accept any sort of restructuring of agreements or price schedules from that company because you’re locked into doing business with them. |
|
|
Cost-performance optimization – Finding the right combination of cloud providers to match your business needs and your checkbook can give your company an extra boost of efficiency while dropping your costs accordingly. |
|
|
Data management – Rather than lump all your data into one cloud, you can diversify to take advantage of the right service for the right function. |
|
|
Power of managed clouds – While the managed clouds take care of specific units, others can serve you best for security or processing purposes. |
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud and Multi Cloud for businesses: [9][10]
|
Hybrid Cloud |
Multi Cloud |
|
Added complexity – It is more complex to manage a Wide Area Network as opposed to a single site’s network or simply utilizing a public cloud’s network. |
Management Complexity – Using services from several cloud vendors increases the complexity of management. |
|
Data transfer bottlenecks – Networking bottlenecks are highly dependent upon the underlying infrastructure and the nature of the packets being sent across the network and with big data, this can easily become a performance bottleneck. |
Complex Structures – The complex structure of heterogeneous environments leads to difficulties in developing cross-platform applications. |
|
|
Security concerns – Additional security concerns and adds new attack vectors for applications. |
|
|
Monitoring complexity – If you use cloud services that include containers, that adds an additional layer of complexity for monitoring. |
|
|
Cost overhead – Adds complexity in controlling cloud spending. |
|
|
Migration challenges – This process will require time and specific skills that aren’t always available in-house. |
What kind of organisation will benefit from the Hybrid Cloud model?
The Hybrid Cloud model is a good choice for e-commerce setups as well as small or big sized corporations handling sensitive data on behalf of their clients. While Public Cloud offers more scalability, Private Cloud ensures security and Hybrid provides the benefits of both. 4
What kind of organisation will benefit from the Multi Cloud model?
Use of multi-clouds are critical for organisations who want to avoid cloud service provider (CSP) lock-in. A multi-cloud strategy enables companies to use best of breed cloud services from the plethora of service providers in the market. 11
Summary of Public vs Private vs Hybrid vs Multi Clouds
Wrapping Up
The choice between public, private and hybrid cloud solutions depends on a variety of factors, use cases and limitations. All cloud models have their own set of limitations and benefits. It completely depends on the requirements of the businesses to pick the right model that fits their purpose and needs. It is not an either/or situation, especially since organisations tend to leverage all four types of cloud solutions considering the inherent value propositions and tradeoffs.
While these concerns and drawbacks are important to address, if catered in controlled environments, utilizing appropriate experts, and resources, the right cloud model can be a total win for your organisation.
Having a hard time finding the right cloud model for your business? We can help!
If you wish to find out more information on Cloud Computing, you can visit us at Netpluz 24/7. Alternatively, you may book an appointment by submitting your information here for a free consultation.
References:
- “What Is Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide: Microsoft Azure.” What Is Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide | Microsoft Azure, azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-cloud-computing/
- Maddox, Teena. “Research: 80 Percent Using or Considering Industry Cloud Services.” ZDNet, ZDNet, 1 Apr. 2015, www.zdnet.com/article/research-80-percent-using-or-considering-industry-cloud-services/.
- Raza, Muhammad. “Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: What’s The Difference?” BMC Blogs, 12 Sept. 2018, www.bmc.com/blogs/public-private-hybrid-cloud/.
- “Public vs. Private vs. Hybrid -Tips to Choose the Best Cloud Model for Your Business.” Impiger, www.impigertech.com/resources/blogs/public-vs-private-vs-hybrid-cloud.
- Dufficy, Tim Pat. “What Is Public Cloud? – Plus the Advantages and Disadvantages for ISVs.” What Is Public Cloud? – Plus the Advantages and Disadvantages for ISVs, www.serverspace.co.uk/blog/blog/public-cloud-plus-advantages-disadvantages-isvs.
- Dufficy, Tim Pat. “What Is Private Cloud? Advantages and Disadvantages.” What Is Private Cloud? Advantages and Disadvantages, www.serverspace.co.uk/blog/what-is-private-cloud-plus-advantages-disadvantages.
- Gupta, Kitty. “Hybrid Cloud vs Multi-Cloud: What You Need to Know.” FreelancingGig, 9 Nov. 2019, www.freelancinggig.com/blog/2019/11/09/hybrid-cloud-vs-multi-cloud-what-you-need-to-know/.
- O’Reilly, Dennis, and Dennis O’Reilly. “Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: A World of Difference – DZone Cloud.” Dzone.com, 1 June 2018, dzone.com/articles/multi-cloud-and-hybrid-cloud-a-world-of-difference.
- “The Hybrid Cloud: Pros and Cons of Hybrid Cloud Computing.” Exit Technologies, 5 Sept. 2019, www.exittechnologies.com/blog/cloud-computing/advantages-disadvantages-hybrid-cloud/.
- User, Super. “Multi-Cloud Computing: Pros and Cons for Enterprise.” Apriorit, ApriorIT, 9 Aug. 2018, www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/552-multi-cloud-computing.
- “Why Multi-Cloud Has Become a Must-Have for Enterprises: Six Experts Weigh In.” Ubuntu, ubuntu.com/blog/why-multi-cloud-has-become-a-must-have-for-enterprises-six-experts-weigh-in.
#cloud #computing #businesses #enterprises #public #private #hybrid #multi #advantages #disadvantages #model
Author: Toh Wei Ting https://sg.linkedin.com/in/tohweiting
The Difference Between Public VS Private Cloud
Businesses are transforming more application are moving into the clouds.
Gartner predicts that by 2021, businesses will adopt an all-in cloud strategy.
When businesses start to use SaaS (Software as a Service), IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and FaaS (Function as a Service), the company must adapt and design their own network architecture in order to be secure.
When businesses are moving to the cloud, it means that they are having a data centre made up of compute and storage resources connected by network somewhere. When you are considering cloud computing solutions for your business, it is better to learn the difference between the types of clouds that you’re going to choose in order to maintain your own secure network architecture.
Nowadays clouds are smart, automated and adaptive. Migrating from the traditional data centre to clouds might improve the efficiency and reduce the cost for your business.
There are two categories of clouds for a growing business, private and public cloud. Public cloud run by the cloud service provider that rent their space for their customers, usually small businesses that only pay as they are using the services. While private cloud usually used by a big enterprise to have their own control in the term of management and customization.
In term of storage and access, public cloud will give access to multiple organizations and will store your data on a shared infrastructure, while in private cloud, your company can have restricted access at a time and dedicated storage infrastructure that is not accessible for others
Using public cloud means that the location of the data centre varies by the public cloud provider’s infrastructure site, while private cloud allows the company to have the freedom to decide and choose, an on-premise data centre or dedicated location on the service provider’s infrastructure.
Having private cloud as your cloud computing solutions might require additional investment for hardware components while on the other hand, public cloud is easy to deploy as they usually do not require additional investment for either hardware or software. The additional investment might cause a company to spend more on hardware to set up on-premise data centres to leverage private cloud services efficiently while using public cloud can help business reduce cost as the company will not need to install anything.
Even if the public cloud is less expensive than private as there is no additional cost, Public cloud has disadvantages when it comes to management, customization and control over the cloud which could be an issue for lack of security.
When a company uses a public cloud, all the data stored in the provider’s data centre and cloud provider is responsible for the management and maintenance process. Having a private cloud give the company more control when it comes to managing their own cloud as they have dedicated administrator to manage the upgrades and installations and this makes it easy to integrate their on-premise or on-cloud applications.
Having a private cloud allows companies to customize their cloud infrastructure according to their business-specific needs and requirements, while the public cloud-only offers a standard operating procedure for organizations.
For scalability, the public cloud offers additional space and infrastructure abilities for their customer and private cloud not only could give incremental space and infrastructure abilities but also offer the customized scalability.
In terms of security, private cloud holds the advantage as all the data and cloud is controlled by a dedicated administrator in a company. Management of private cloud can be customized and enhanced to implement higher levels of authentication and security for the cloud environment.
This power to control the cloud environment helps the company to easily add and remove users and have a strict policy on who can access which data and what the users can do inside the cloud. While easy to deploy public cloud can only have standard security protocols that controlled by the cloud provider.
While big enterprise might opt for a private cloud and small business prefer to go with a public cloud, there is also a solution to have the best of both cloud, which is a hybrid cloud. Hybrid cloud can be the solution for a company that wants to remain their network environment secure by having the most sensitive applications in the private cloud while storing the other forms of applications in a public cloud service provider.
If you are having a problem to decide which cloud environment that suitable for your business model, you can contact Netpluz for a free consultation on your cloud computing needs. Netpluz is MTCS SS 584 compliant. Our team have a commitment to ensuring sound operational and security control across all computing services.
The Multi-Tier Cloud Security (MTCS) Singapore Standard (SS)584 is a cloud security certification managed by the Singapore Info-comm Media Development Authority (IMDA).
The MTCS SS is the world’s first cloud security standard that covers multiple tiers. With the new standard, certified CSPs will be able to spell out the levels of security that they can offer to their users.
Businesses that rely on cloud computing services will also be able to use the MTCS SS to better understand and assess the cloud security they require.
Tier-based cloud security standard.
The Multi-Tier Cloud Security (MTCS) Singapore Standard (SS)584 is a cloud security certification managed by the Singapore Info-comm Media Development Authority (IMDA).
The MTCS SS is the world’s first cloud security standard that covers multiple tiers. With the new standard, certified CSPs will be able to spell out the levels of security that they can offer to their users.
MTCS SS has a self-disclosure requirement for CSPs covering service-oriented information that is normally included in Service Level Agreements. This covers areas such as data retention, data sovereignty, data portability, liability, availability, business continuity, disaster recovery, as well as incident and problem management.
Businesses that rely on cloud computing services will also be able to use the MTCS SS to better understand and assess the cloud security they require.
The scope of services included in the certification highlights Netpluz‘s ongoing and continuous commitment to ensuring sound operational and security controls across all Cloud Computing services, such as:
- Private Cloud
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
- Backup as a Service (BaaS)
Netpluz Cloud Platform is certified as MTCS compliant.
For more information, please contact us directly at contact@netpluz.asia or click here.